-
-
Humanized model of the immune system
-
iHuPBMC-T
-
iHuPBMC-NK
-
iHuPBMC-B
-
PBMC-LT
-
CD34+ HSC
-
Winn model
-
iHuPBMC-MHC/KO
-
iHuPBMC-OncVax
-
PBMC mixed inoculation model
more -
-
In vivo tumor experimental platform
-
CDX
-
iHuPDX
-
Non-GLP Toxicology
-
PK/PD
-
Brain in situ model
-
Other in situ models
-
Hematologic tumor model system inoculation
-
Creation of high interstitial tumor models
more -
-
In vitro killing experiment platform
-
Immune co-culture killing model
-
CDC
-
In vitro killing experiment platform
-
IC50
-
PDC High-Throughput In Vitro Pharmacodynamics
-
3D organoids
-
ADCC
-
T cell-mediated killing experiment
more -
-
Mouse-derived immune system model
more -
Tumor vaccine
more -
Cell therapy
more -
In vitro testing platform
more -
Non-GLP Toxicology Platform
more -
Non-tumor model and drug efficacy evaluation platform
-
Systematic Vaccination Model
-
Non-tumor model and drug efficacy evaluation platform
-
Skin injury model
-
Stroke model
-
Liver fibrosis model
-
Diabetes model
-
Gouty Arthritis (GA) Model
-
Pulmonary fibrosis model
-
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) model
-
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) model
-
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) Model
more -
-
-
-
PDX model
-
PDX model
-
Head and neck cancer
-
Eye cancer
-
Lung cancer
-
Human breast cancer
-
Esophageal cancer in humans
-
Human gastric cancer
-
Colorectal cancer
-
Human liver cancer
-
Bile duct cancer
-
Gallbladder cancer
-
Human pancreatic cancer
-
Human kidney cancer
-
Human Bladder Cancer
-
Ureteral cancer
-
Prostate cancer
-
Uterine cancer
-
Cervical cancer in women
-
Human Ovarian Cancer
-
Human skin cancer
-
sarcoma
-
Human Nervous System Cancer
-
Embryonal carcinoma
-
Human Lymphoma
-
Human leukemia
-
Multiple Myeloma
-
Adrenal gland
-
Mesothelioma
-
Other people
more -
-
CDX model
-
CDX model
-
Head and neck cancer
-
Eye cancer
-
Lung cancer
-
Human breast cancer
-
Esophageal cancer in humans
-
Human gastric cancer
-
Colorectal cancer
-
Human liver cancer
-
Bile duct cancer
-
Gallbladder cancer
-
Human pancreatic cancer
-
Human kidney cancer
-
Human Bladder Cancer
-
Ureteral cancer
-
Prostate cancer
-
Uterine cancer
-
Cervical cancer in women
-
Human Ovarian Cancer
-
Human skin cancer
-
sarcoma
-
Human Nervous System Cancer
-
Embryonal carcinoma
-
Human Lymphoma
-
Human leukemia
-
Multiple Myeloma
-
Adrenal gland
-
Mesothelioma
-
Other people
more -
-
Homogeneous Model
-
Homogeneous Model
-
Head and neck cancer
-
Eye cancer
-
Lung cancer
-
Breast cancer
-
Stomach cancer
-
Liver cancer
-
Bile duct cancer
-
Gallbladder cancer
-
Pancreatic cancer
-
Kidney cancer
-
Bladder cancer
-
Ureteral cancer
-
Prostate cancer
-
Uterine cancer
-
Cervical cancer
-
Ovarian cancer
-
Esophageal cancer
-
Skin cancer
-
sarcoma
-
Nervous System Cancer
-
Embryonal carcinoma
-
Lymphoma
-
Leukemia
-
Multiple Myeloma
-
Adrenal gland
-
Mesothelioma
-
Other
-
Colorectal cancer
more -
-
New Drug Development Services
Gouty arthritis (GA) model
Gout is a disease caused by the deposition of monosodium urate (MSU) crystals in joints, body fluids, and tissues due to high levels of uric acid in the blood. When deposited in the periarticular soft tissues and within the joints, it causes painful inflammation, known as gouty arthritis (GA), the most common manifestation of gout. This is characterized by red, swollen joints, acute and recurrent attacks, and can even lead to chronic arthritis and joint damage.
Case Presentation:
1. Modeling Method:
MSU deposition is a key factor in gouty arthritis. When MSU crystals deposit in the joints, they are recognized as "foreign bodies" by leukocytes. Leukocytes attempt to phagocytose these crystals, but this process triggers a series of inflammatory responses, releasing various inflammatory mediators such as cytokines and complement systems, leading to acute gout symptoms such as joint pain, swelling, redness, and fever. Therefore, gout animal models are mainly prepared by a single injection of MSU crystals into the joint cavity, which closely mimics clinical symptoms. This model can be used to study the in vivo pharmacodynamics of anti-gouty arthritis drugs.
2. Animal Species:
Adult female SD rats
3. Detection Indicators
(1) General observation;
(2) Joint swelling detection;
(3) Joint inflammation and impairment scoring (can be customized according to client needs);
(4) Analysis of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-8, etc., in joint fluid (can be customized according to client needs);
(5) Joint tissue immunohistochemistry and pathological examination (can be customized according to client needs).
4. Results
(1) Body weight
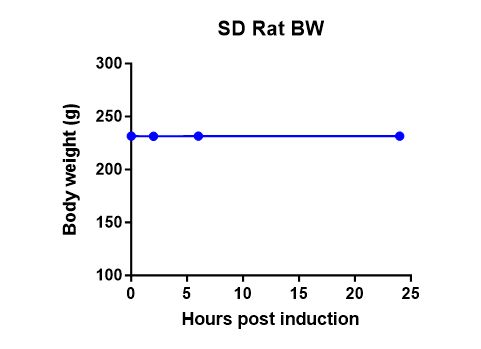
(2) General observation
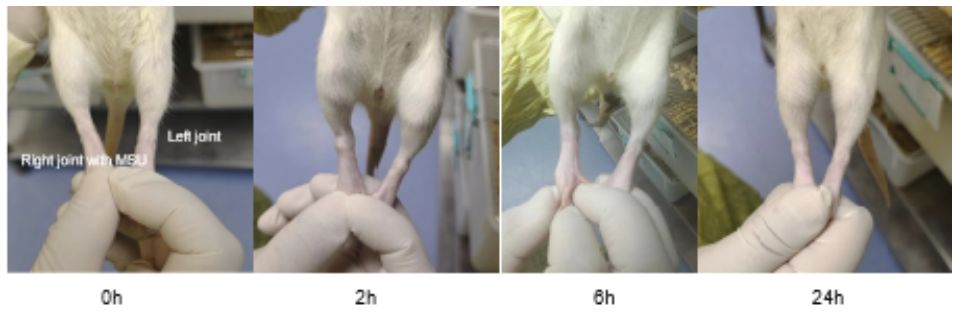
(3) Joint swelling (joint circumference):
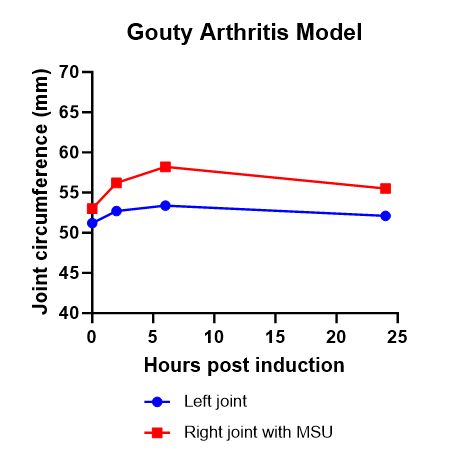
Compared with before induction, both joints showed swelling, but the MSU-injected side showed more significant swelling. The swelling gradually returned to the pre-induction state after 24 hours.
InnoModels Biotechnology (Beijing) Co., Ltd.
-
TEL: +86 15711355061
-
E-mail: xuyl@imodels.tech
-
Address: Building 14, No. 79 West Shuangying Road, Changping District, Beijing
COOKIES
Our website uses cookies and similar technologies to personalize the advertising shown to you and to help you get the best experience on our website. For more information, see our Privacy & Cookie Policy
COOKIES
Our website uses cookies and similar technologies to personalize the advertising shown to you and to help you get the best experience on our website. For more information, see our Privacy & Cookie Policy
These cookies are necessary for basic functions such as payment. Standard cookies cannot be turned off and do not store any of your information.
These cookies collect information, such as how many people are using our site or which pages are popular, to help us improve the customer experience. Turning these cookies off will mean we can't collect information to improve your experience.
These cookies enable the website to provide enhanced functionality and personalization. They may be set by us or by third-party providers whose services we have added to our pages. If you do not allow these cookies, some or all of these services may not function properly.
These cookies help us understand what you are interested in so that we can show you relevant advertising on other websites. Turning these cookies off will mean we are unable to show you any personalized advertising.
InnoModels Biotechnology (Beijing) Co., Ltd

